In a general annuity, the payment frequency and the compounding frequency are not equal ([latex]P/Y \neq C/Y[/latex]). In this situation, the given interest rate must first be converted to the equivalent interest rate where the new compounding frequency equals the payment frequency. Using the equivalent interest rate, calculate the periodic interest rate [latex]i_2[/latex].
Components of a Present Value Calculation
Understanding the present value of an annuity allows you to compare options for keeping or selling your annuity. These reviewers are industry leaders and professional writers who regularly contribute to reputable publications such as the Wall Street Journal and The New York Times. In our illustrative example, we’ll calculate an annuity’s present value (PV) under two different scenarios. By submitting this form, you consent to receive email from Wall Street Prep and agree to our terms of use and privacy policy.
Table of Contents
- Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia.
- In simpler terms, it tells you how much money the annuity will be worth after all the payments are received and compounded with interest.
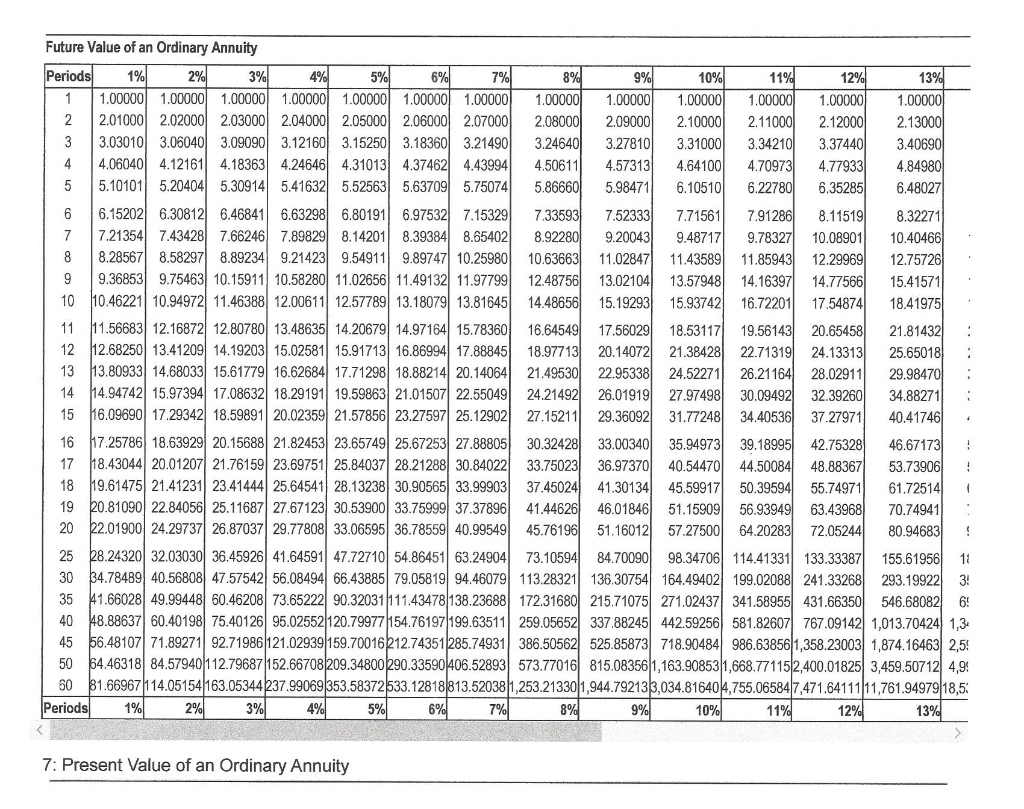
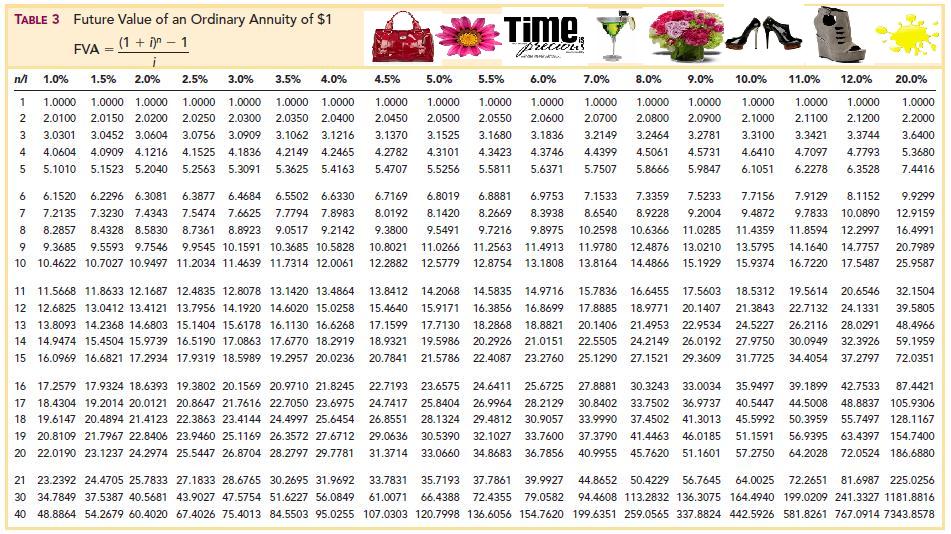
- You can then look up the present value interest factor in the table and use this value as a factor in calculating the present value of an annuity, series of payments.
- You may hear about a life annuity, where payments are made for the remaining lifetime of the annuitant (the person who receives the annuity payments).
The buttons provide various financial calculations and standard calculator functions. The time value of money buttons are located in the [latex]TVM[/latex] row (the third row from the top) of the calculator. The five buttons located on the third row of the calculator are five of the seven variables required for time value of money calculations. This row’s buttons are different in colour from the rest of the buttons on the keypad.
Ask Any Financial Question
It is calculated using a formula that takes into account the time value of money and the discount rate, which is an assumed rate of return or interest rate over the same duration as the payments. The present value of an annuity can be used to determine whether it is more beneficial to receive a lump-sum payment or an annuity spread out over a number of years. The present value of annuity is the current worth or cost of a fixed stream of future payments. This can be calculated using various financial tools, including tables and calculators, which are available on the web or in books of tables. Many websites, including Annuity.org, offer online calculators to help you find the present value of your annuity or structured settlement payments.
It’s a tool for planning how much you’ll accumulate by consistently contributing to a retirement plan or understanding the total repayment amount for a loan with regular installments. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you. John Egan is a veteran personal finance writer whose work has been published by outlets such as Bankrate, Experian, Newsweek Vault and Investopedia. So, let’s assume that you invest $1,000 every year for the next five years, at 5% interest. Imagine you have $1,000 right now and you deposit it into a high-yield savings account offering a 1% annual interest rate.
The Annuity Formula for the Present and Future Value of Annuities
To use an annuity table effectively, you first need to determine the timing of your payments. Are they received at the end of the contract period, as is typical with an ordinary annuity, or at the beginning? Because most fixed annuity contracts distribute payments at the end of the period, we’ve used ordinary annuity present value calculations for our examples. It’s important to note that the discount rate used in the present value calculation is not the same as the interest rate that may be applied to the payments in the annuity. The discount rate reflects the time value of money, while the interest rate applied to the annuity payments reflects the cost of borrowing or the return earned on the investment.
By calculating the present value of an annuity, individuals can determine whether it is more beneficial for them to receive a lump sum payment or to receive an annuity spread out over a number of years. This can be particularly important when making financial decisions, such as whether to take a lump sum payment from a pension plan or to receive a series of payments from an annuity. An individual cash flow or annuity can be determined by discounting each cash flow back at a given rate using various financial tools, including tables and calculators. The “present value” term refers to an individual cash flow at one point in time, while the term “annuity” is used more generally to refer to a series of cash flows. The present value of an annuity is the amount of money needed today to cover future annuity payments.
On the other hand, the future value of an annuity will be greater than the sum of the individual payments or receipts because interest is accumulated on the payments. Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products.
Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. The trade-off with fixed annuities is that an owner could miss out on any changes in market conditions that could have been favorable in terms of returns, but fixed annuities do offer more predictability. An Annuity is a type of bond that offers a stream of periodic interest payments to the holder until the date of maturity. Assuming that the term is 5 years and the interest rate is 7%, the present value of the annuity is $315,927.28. Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia.
“Essentially, a sum of money’s value depends on how long you must wait to use it; the sooner you can use it, the more valuable it is,” Harvard Business School says. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided affordable care act and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
